|
PVC certainly is one of the most versatile
plastics even though it has lost its premier
position to PP in the nineties. PVC is still
consumed at about 30 million tons out of the
total of 165 million tons in 2003. PVC therefore
has almost 20% share of the global plastic consumption.
While polyolefins are the first material of
choice for packaging, PVC still continues to
be the major building block for construction
application segment.
PVC enjoys practically 2/3rd share of the pipe
and wire/cable applications. Both these applications
are characterized by their usage for quite a
long time. Both pipes and wire/cable have normally
more than 25 years of safe usage. PVC therefore
does not surface in the waste/recycling as much
as polyolefins. Another interesting aspect of
PVC is that it has possibly the widest range
of processing techniques compared to all other
polymers. Calendering as well as paste techniques
like spread coating, slush moulding and dip
moulding are predominantly used for PVC. What
is most remarkable that the applications of
PVC cover a very broad spectrum of products
that have either very high flexural modulus
(such as pipe or building profile) or high flexibility
(such as footwear or refrigerator liners or
several soft gaskets/profiles).
There are essentially four polymerization techniques
that are used for manufacture of PVC polymer,
but suspension is by far the largest process
that is employed. Suspension process accounts
for about 90% of the global production of 30
million tons. Emulsion and mass processes although
provide some specific advantages to PVC are
growing at almost half the rate compared to
suspension polymer. Solution process has a very
small role to play for coating application.
PVC homopolymer has the largest market share and possibly accounts for almost 95% of the global PVC. There are many copolymers or specialties but are almost losing their share.
PVC is predominantly an amorphous material
because of its predominant stactic structure.
However it can contain about 5-10% of crystalline
particles due to the presence of syndiotactic
structure. Higher molecular weights can contain
higher level of crystalline particles compared
to lower molecular weight. This crystalline
phase can affect the properties of PVC product
that contains lower level of plasticizer. In
fact, those PVC products having Shore hardness
beyond 97 and Shore D hardness between 30-40
are quite prone to the effect of the crystallinity.
The mechanical properties of such products could
have very wide variations due to different levels
of crystallinity.
Molecular weight is defined by primarily 3 different
values. They are :
(1) K value (2) Relative/Inherent viscosity
or viscosity number (3) Mean polymerization
degree.
The correlation between these three properties
and molecular weights are given in Table 1.
Figure 1 shows the relationship between K value
and Viscosity Number.
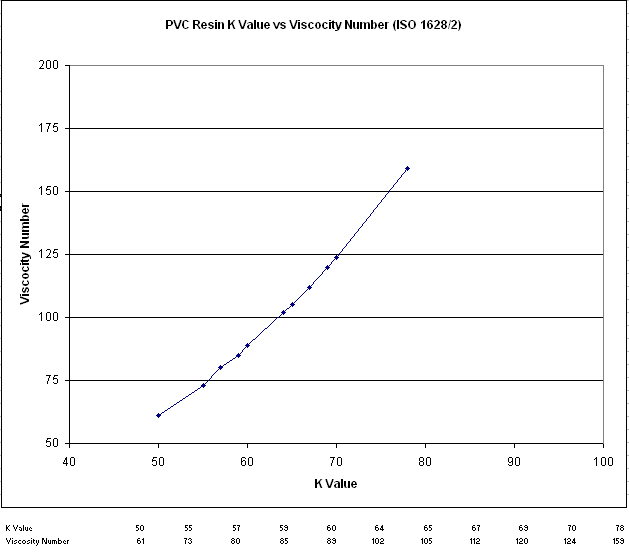
Medium molecular weight ranging from K value of
60-67 is more widely used compared to low molecular
as well as high molecular weights. Low molecular
weight polymer grades are used for rigid products
while very high molecular weight grades are
used to obtain special properties like matt
surface finish or better toughness. Commercially
low molecular weights are available with K values
in the range of 45-50 and extra high molecular
weights have K values in the range of 80-104.
However, the commercial usage of both these
grades is only in niche products and therefore
they have a share of less than 5%.
Molecular weight distribution in PVC is in a narrow range of 2-4 and has possibly much less pronounced effect on the processing as well as performance of PVC products.
Compared to the effects of structure of PVC,
its particle morphology plays an important role
in processing and performance of products. The
emulsion grades designed for spread coating
have the most narrow particle size (4 micron)
while the pipe grade suspension grade has the
coarsest particle size, since pipe is processed
from dry blend. The particles are tuned finer
or coarser according to the applications. For
instance clear rigid PVC products like film
or bottle have finer particle size range to
achieve excellent dispersion of additives and
attain clarity. Besides, the morphology of particles
plays an important role. For instance, the emulsion
grade polymer has solid spherical particles
with in a narrow particle range. Addition of
plasticizers to such polymer results into a
formation of paste. On the other hand the particles
for wire/cable as well as plasticized clear
products require uniformly hollow particles
to achieve excellent plasticizer dispersion.
In fact the uniform porosity is a prime requirement
of all plasticized applications. The particles
of spherical nature provide ease of dispersion
of additives. Bulk density of PVC polymer is
an important characteristic that helps in its
selection for different applications. For instance
polymer grades ideally suited for plasticized
applications have bulk density on a lower side
(less than 0.53) while grades for pipes have
bulk density on a higher side (> 0.56).
Fish eyes are quite commonly observed in PVC polymer
because of presence of gel (higher molecular
weights). These are objectionable and cannot
be acceptable for specific applications such
as thin wire or clear film/bottle. These fish
eyes are controlled during polymerization and
good manufacturing practice help in achieving
“fish eye” free grades. It is therefore
advisable that the processors of good quality
clear products or wire products screen PVC batches
for fish eye rating by conducting film-blowing
test.
The purity of PVC polymer not only affects the
clarity or creates fish eyes but also cause
deterioration of electrical properties. For
such critical applications it is important to
regularly conduct quality control test on the
incoming PVC for purity. One of the simple tests
used for wire/cable is determination of conductivity
of water extract. This value signifies the impurity
of material that is soluble in water.
PVC is typically manufactured with water as
a heat dissipation medium. The resultant PVC
polymer tends to have some residual water/moisture
that has not got evaporated even after drying.
During storage PVC tends to absorb some more
moisture. Higher level of moisture (more than
0.3%) interferes with performance of finished
product. It is essential that more care be taken
to prevent ingress of moisture during storage
particularly in humid condition.
PVC is generally produced either by batch process or by semi continuous process. It is therefore quite difficult to achieve very uniform properties in every batch. For achieving more uniform properties of finished product, it is necessary not to mix more than one batch. The batch segregation would result into better products.
The selection of PVC polymer grade is very
important for different products. The wrong
usage of PVC grade calls for doom. It is very
important that processors always select the
correct grade for application.
This article focuses on the characteristics
of PVC polymer for more sensitive end products.
PVC polymer manufacturers can provide more guidance.
The environmental issues have caused concerns on growth of PVC over the last three decades. The scientists and researchers involved in PVC always have come up to resolve these problems regularly. PVC therefore continues to grow at least at the global GDP growth of about 2.5-3%. It is expected that it will continue to do so even when the overall polymer would grow at about 5-6%
|
