|
|
|
|
 |

Adhesives find higher usage in automotive industry |
 |
|
| |
The adhesives and sealants industry includes two chemically similar but functionally different groups of formulated products. Adhesive products are used to create a bond between two different or similar materials while sealants are used to create an impenetrable barrier to gas or moisture. Adhesives and sealants are made from precise blends of resins, synthetic rubber elastomers, and agents or additives used to enhance certain characteristics, depending on the end use. Industries that typically use adhesives and sealants include automotive, construction, consumer products, assembly, packaging and labeling.
Adhesives and sealants find several applications in an automobile. In fact, adhesives have revolutionized the way automobiles have been designed and built. Adhesives are used to assemble metal, glass, plastics, rubber, and a variety of other materials during the manufacture of automobiles. Adhesives help prevent the ingress of water, salt and dirt in the car body shell. The shell layers, most commonly steel, are coated with a number of oils used for protection and lubrication as they are cut and stamped to shape. Good adhesion performance must be maintained over a wide range of test temperatures, typically from -30�C to +90�C and after several types of ageing tests. In addition to their key purpose of fastening, they may be used to seal, damp vibrations, be electrically insulating or conducting, provide corrosion resistance, or perform a variety of other functions; depending on the application. Adhesive bonding reduces steps in the manufacturing processes, which ultimately results in reduced cost.
They are routinely used in both structural and non-structural automotive applications. Epoxy and PU sound deadening materials and structural adhesives are now used between body shell layers instead of mechanical fasteners. This lowers a car's weight, improving fuel efficiency along with reducing the likelihood of corrosion. Adhesives also offer better aesthetics as compared to mechanical fastening. Adhesive joints can show higher strength and stress dispersion than other attachment methods in automobiles. Epoxy adhesives are used for load carrying members and areas where aesthetic constraints demand perfect joint stability as they provide the stiffest bond. PU is used where elasticity is required, as in vibration damping or shock absorption while acrylate adhesives offer balance properties. Hot melt adhesive is gaining higher share of the automotive industry due to emission problems of elimination of volatile organic compound. Water based adhesives are also gaining higher penetration.
The application and processing characteristics of an adhesive represent, perhaps, the greatest value to the automobile manufacturer as they enable cost efficient designs.
As per a report by Sri Consulting, the polymer dispersion/emulsion adhesives category is the largest because of their versatility and moderate price, followed by solvent-based adhesives. Consumption of solvent-based adhesives is on the decline in developed countries primarily because of VOC emission regulations, but is growing strongly in developing countries such as China following the rise of shoe manufacturing. Silicone products dominate the sealants market, followed by polyurethane products. Polysulfide sealants are losing market share to these products and to commodity sealant products. Silicon-modified polyether sealants have expanded beyond their Japanese production base to the larger markets in North America and Western Europe.
The following pie charts show world consumption of adhesives and sealants.
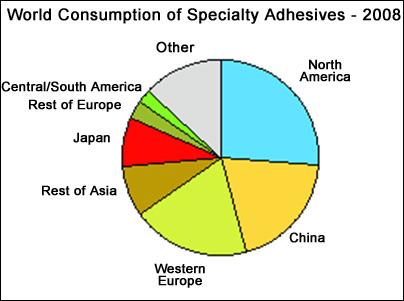
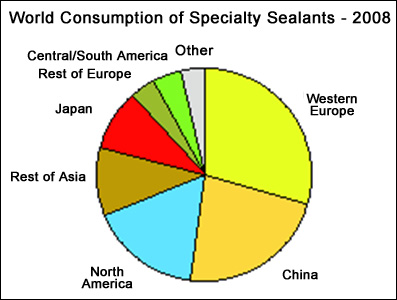
Significant increases in price of petroleum-derived feedstocks have impacted adhesive and sealant producers. Typically producers with valuable brands have exercised pricing power and tried to maintain margins during rising raw material prices although this was exceptional during the economic recession in 2008 since raw material price increases tended to outpace adhesive and sealant price increases, particularly in H1-2008. Consolidation in the adhesives and sealants industry has built depth in vertical integration and broadened product lines in some major companies such as Henkel, while other companies have shut down, spun off poorly performing or less related businesses or reduced the array of products offered, such as General Electric and H.B.Fuller. However, the industry remains highly fragmented, with numerous small and medium-sized companies with a relatively high level of customization and service, particularly in the highest-value adhesive and sealant segments. The cost of producing adhesives and sealants is attributable primarily to the cost of the raw materials along with the requisite service component of training customers and helping them resolve manufacturing issues. Adhesives compounding equipment is typically installed in multipurpose units that are seldom dedicated to a specific product. Important strengths in manufacturing are flexibility, low-cost production units and appropriate quality control. In general, the adhesives business is highly competitive, especially in the commodity sector. Prices and margins vary, depending on the specific adhesive or sealant, market segment, and regional market. In general, gross margins for adhesive products commonly range from 15-25% for commodity products, while specialty products can range to as much as 45-50% or more. Environmental regulations continue to increase as more VOC emission sources are targeted for reduction or elimination. Some producers have switched from targeted solvents to other solvents only to find they must switch again with new regulations, or have changed to lower or no-emission technologies. Waterborne products continue to push into commodity markets, but their penetration into specialty segments has slowed because of the formulating difficulties and performance challenges in the solvent borne segments. Although the consumption of solvent-based adhesives is continuing to decline in North America, Western Europe and Japan, this category is growing steadily in China and the rest of Asia, following the growth of relocated industries such as shoe manufacturing. Overall, hot melt technologies have seen the greatest growth globally, because they offer very low or no emissions, work on a variety of substrates, and are easy to apply. Also, new low-temperature and reactive hot melt products have expanded the possible end-use areas for these adhesives.
|
|
| | | | | | |

{{comment.DateTimeStampDisplay}}
{{comment.Comments}}