
| Foams are becoming attractive not only for reduced material consumption, which in turn lowers the cost of production, weight reduction and fuel savings but also; for developing a spectrum of new properties, which are the critical to qualities of specific applications. Polymer foam is polymer matrix with either air bubbles or air tunnels incorporated in it, known as either closed-cell or open-cell structure. Closed-cell foams are generally more rigid, while open-cell foams are usually flexible. Foams in the area of damping devices like in sports equipment or accessories which are exposed to high level of impact, can be manufactured with specially filled fluids called Shear thickening fluids (viscosity of fluids increases with increase in shear rate or stress). In building and construction for sealing and thermal insulation applications closed cell, sometimes crosslinked foams are being utilized. | ||
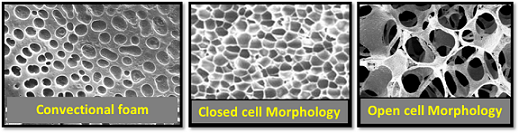 Different foam morphologies and their targeted applications. |
||
|
||
| Polymer material engineering for development of foam products and Pilot plant facilities at IITD. | ||
| The key to production of foams which meet specific requirements lies in proper selection of raw material as well as process parameters, the latter governing the volume expansion, cell size and distribution as well as the open cell content. At IIT Delhi, research is being carried out to investigate and develop the effect of compositional change and processing parameters on the foamability of various polymers, such as, PP (commodity polymer), PLA (biopolymer and biodegradable) and various of their blends & nanocomposites by using physical blowing agents. Targeted foamed materials are also developed through various foam characterization techniques. | ||
|
Previous Article
Next Article
{{comment.DateTimeStampDisplay}}
{{comment.Comments}}