
|
In 2012, the worth of the global polymer foams market was US$82.6 bln and is estimated to reach US$131.1 bln by 2018, growing at a CAGR of 7.7% from 2013 to 2018. High demand across industries such as automotive, building & construction and packaging will increase the overall polymer foam consumption, as per MarketsandMarkets. Polymer foam types are significantly penetrating their applications market. They have different characteristics as per the manufacturing and their application requirement in the end products. The Asian market is expected to dominate, with its growing demand for foams in different applications especially building & construction. The Western European and North American markets are expected to show a rising growth in the next five years with allied industries expected to stabilize the overall business need in respective regions. Polyolefin foams are expected to penetrate the global market with the highest growth within competitive foams available in the market. Polyurethane foams are dominant in consumption and revenue made, reasoned by its optimal cost to performance factor.Asia-Pacific is the largest region, both in terms of volume and value, followed by Western Europe and North America. U.S., Germany, U.K., Brazil, Russia, China, and India are expected to persist as successful foam markets. Eastern and Central European nations, emerging South-East Asian and nations that host the Olympics and other events would supplement the growth of polymer foams. An increase in auto sales, proposals for improvement of infrastructure and rising housing market in emerging economies will drive the polymer foams market. BCC Research forecasts an overall compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 2.5% for all foams produced from commercial plastics for 2010-2015. This market is valued at 7.5 bln lbs in 2010 and is expected to reach nearly 8.6 bln lbs in 2015. Polyolefins, both polyethylenes and polypropylene foams, have a growing market of about 443 mln lbs in 2010. A higher compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.8%, and a value of 509 mln lbs, is forecast for 2015, based on increasing demand for cross-linked polyethylene foams in several applications. Polyurethane (PUR) foams, both flexible foams used primarily for cushioning and rigid foams used mostly for thermal insulation, have the largest market, 3.9 bln lbs in 2010, with a predicted compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.6% to 4.4 bln lbs in 2015. 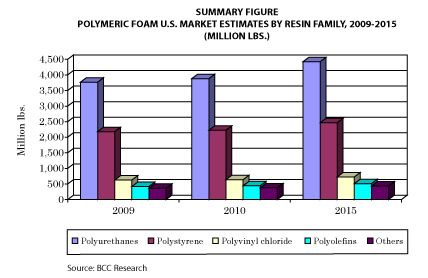 According to a report from Global Industry Analysts, the worldwide annual production of polymeric foams will reach 18 mln tons in the next five years. Such foams come in two varieties - high-density cellular plastics and low-density foams - and each has its own unique applications. Within the low-density foam subset, polyurethane foams provide the base material for most spray foam insulation. Indeed, the insulation sector has apparently kept that part of the industry afloat, even as demand for other applications of low-density polyurethane foam dropped off. Despite the adverse conditions, potential opportunities exist owing to sustained demand for spray polyurethane foam in industrial and residential applications. Asia-Pacific offers vast growth potential for polyurethane foams. GIA also identifies the growing trend towards green building and sustainable development as an important backstop for the foam industry. While real estate may still be recovering from the subprime mortgage meltdown, the rising cost of energy and awareness of the consequences of climate change mean that a greater share of new structures emphasize efficient, sustainable construction. Sprayed polyurethane foam is simply a subset of the overall Polymeric Foam category growth, but the future is still very bright for polyurethanes. Polymeric foams are ubiquitous in their application and versatile in function, with high-density cellular plastics finding widespread use in furniture, transportation, and building products while low-density foams are employed in shock absorption, insulation, and rigid packaging. Foams exhibit superior insulating properties, impact-resistant characteristics, buoyancy, and outstanding strength-to-weight ratios, among other attributes. The global economic crisis led to a decline in demand for polymeric foams across most countries during the years 2008 and 2009. Sluggish demand forced several manufacturers to either close some of the plants or shut down all operations. Majority of the countries are forecast to witness sluggish growth in the imminent future. Growth is favored by the emergence of applications such as foamed PVC for windows/doors, house siding and construction shapes, and cross-linked polyolefin foam in sports and leisure goods. The continuous focus on sustainable, green construction products is likely to fuel growth in the polymeric foams markets. The need to comply with new regulatory specifications and secure certifications is expected to create growth opportunities for manufacturers. Asia Pacific constitutes the largest and fastest growing regional market for Polymeric Foams. The recession resulted in a considerable decline in demand for polyurethane foams across the world, owing to falling consumption in downstream industries and increase in prices of feedstock. Despite the adverse conditions, potential opportunities exist owing to sustained demand for spray polyurethane foam in industrial and residential applications. Asia-Pacific offers vast growth potential for polyurethane foams. Demand for polyolefin foams is driven primarily by increasing the use of cross-linked polyethylene in applications such as sports and leisure goods. Flexible foams are used primarily for cushioning while rigid foams find widespread use in thermal insulation. However, growth would be tempered due to environmental concerns regarding use of PVC. |
Previous Article
Next Article
{{comment.DateTimeStampDisplay}}
{{comment.Comments}}