
| 2008 saw stagnant growth of plastics machinery sector in Europe due to the global economic meltdown. A weak economy, leading to weaker plastic demand in almost all application sectors saw major Europe�s plastic machinery business flatten in 2008. Exports remained at the same level at about 50% of the total sales in 2008, bailing out the industry to great extent. Very feeble demand was seen in 2009 in the European countries as well as in the export market, particularly with the weakening of the automotive and building/construction sector. EUROMAP's overall result for the year 2008 was positive. Despite modest increase rates, a gain of 1.2% in total production, and of 1.5% in exports, 2008 figures marked record values. While core machinery as well moulds & dies grew at 1% and 1.5% respectively (showing a stable pace), peripheral equipment was up at 4.1%. Only flexographic printing machines displayed negative growth at -7%. EUROMAP's share in 2008 of the global market remained beyond 50% in world production and grew to a peak value of 57% in world exports based on a declining overall export volume. Drop in demand from the automotive suppliers' sector was impacted first and most noticeably. National scrappage schemes temporarily prevented the worst. Overall demand from customers in the field of construction was weak except for insulation. Packaging, too, was affected albeit packaging of consumer goods has developed better than industrial packaging. Medical applications proved to be a constantly growing market for plastics. The slowdown in 2009 which Europe's plastics and rubber equipment manufacturers had predicted turned out to be deeper than expected. During H1-09, exports of European manufacturers of plastics and rubber machinery to Eastern Europe, North and Latin America decreased on a large scale. Demand from customers in Asian countries could not compensate the loss. According to official statistics of German and Italian plastics and rubber machinery manufacturer�s average export is down 35%. Overall production is expected to fall by about 22% in 2009. The total EUROMAP production volume should thus decrease to approximately �13.6 bln. The strongest decrease expected by member countries is for the core machinery business at about 30%; this sector holds the biggest share at 62.7%. The association assumes that the decline in orders has now bottomed out. Sentiment and business expectations in the plastics and rubber converting industry have improved recently. Though demand for plastics and rubber machines slowly seem to be on the increase again, financing remains an obstacle. The industry expects an upward trend in time for the K 2010 at the latest. 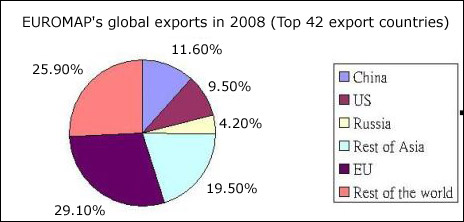 After last year's slump of 30%, the German plastics and rubbery machinery industry is set to achieve sales growth of more than 11% in 2010, with just fewer than 11% growth expected for 2011. Growth is largely driven by foreign demand, particularly from Asia, as per VDMA Plastics and Rubber Machinery Association. Despite these growth rates, the country will still be 25% below all-time high recorded in 2008. The growth has occurred against a backdrop of major risks that include the fragile state of the financial markets and the danger of overheating in the emerging economies, particularly China and India. Increasing energy and raw materials prices, especially for crude oil, may also jeopardise the recovery. Also, the extent to which the current economic upturn is attributable to fiscal measures, such as the economic stimulus programs, remains unclear. In this scenario, the weakness of the euro is likely to offer support and create opportunities for the export-oriented plastics and rubber machinery industry. Over 35% of Germany�s total exports of plastics and rubber machinery was to Asia in 2009. Asia�s share of the total increased from 29.1% to 36.5%. In terms of volume, exports to Asia fell by 17.2%. With growth of 19.6%, exports to Central and South Asia were the only real bright spot on the entire export horizon. Deliveries to South East Asia were only slightly lower than 2008, recording a drop of 3.6%. Those to the near and Middle East fell by 21.4%, while East Asia was down by as much as 26.2%. What was gained in Asia was lost in the 27 countries of the EU- Their share was down from 35% to 29.6%. German exports of plastics and rubber machinery fell by 33.9% in 2009. Federal Statistical Office figures show that they amounted to �2637 mln. The previous year they had risen by 4.6% to a record total of �3989 mln. The collapse affected the major sales regions and all important markets to much the same extent. In Central America (down 20.6%) the decline was less marked than in the 27 EU countries (down 44%), the rest of Europe (down 41.5%), North America (down 38.7%) or South America (down 39.5%). The rest of Europe, North America and Africa all recorded slightly lower totals, declining from 13.8 to 12.2%, from 11.6 to 10.7% and from 2.7 to 2.6% respectively. Latin America's share grew marginally, from 7.1 to 7.2%. Imports from foreign plastics and rubber machinery manufacturers to Germany declined by 36.7% to �539 mln. Import demand had not been this low since 2002 and 2003, leading to a marginal increase in the German balance of trade surplus in plastics and rubber machinery. |
Previous Article
Next Article
{{comment.DateTimeStampDisplay}}
{{comment.Comments}}